1.1 初识ElasticSearch | 《ElasticSearch入门到实战》电子书 (chaosopen.cn)
目录
第一章 入门
ElasticSearch结合Kibana、Logstash、Beats,是一整套技术栈,被叫做ELK,因此下载时版本要对应一致。
1.1 ElasticSearch需求背景
假设一个电商项目,商品的搜索肯定是访问频率最高的页面之一。目前搜索功能是基于数据库的模糊搜索来实现的,存在很多问题。
首先,查询效率较低。
由于数据库模糊查询不走索引,在数据量较大的时候,查询性能很差。
需要注意的是,数据库模糊查询随着表数据量的增多,查询性能的下降会非常明显,而搜索引擎的性能则不会随着数据增多而下降太多。目前仅10万不到的数据量差距就如此明显,如果数据量达到百万、千万、甚至上亿级别,这个性能差距会非常夸张。
其次,功能单一
数据库的模糊搜索功能单一,匹配条件非常苛刻,必须恰好包含用户搜索的关键字。而在搜索引擎中,用户输入出现个别错字,或者用拼音搜索、同义词搜索都能正确匹配到数据。
综上,在面临海量数据的搜索,或者有一些复杂搜索需求的时候,推荐使用专门的搜索引擎来实现搜索功能。
1.2 ElasticSearch 和关系型数据库的对比
在Elasticsearch 7.x中,Type的概念已经被删除了,就是一个索引下面只能有一种类型。
1.3 基础概念
文档和字段
对标数据库,行为文档,列为字段 。
elasticsearch是面向文档(Document)存储的,可以是数据库中的一条商品数据,一个订单信息。文档数据会被序列化为json格式后存储在elasticsearch中:
索引和映射
对标数据库,表为索引,索引中文档的字段约束为映射。
随着业务发展,需要在es中存储的文档也会越来越多,比如有商品的文档、用户的文档、订单文档等等:
所有文档都散乱存放显然非常混乱,也不方便管理。
因此,我们要将类型相同的文档集中在一起管理,称为索引(Index)。例如:
第二章 索引操作
ES索引是存储数据的容器,类似于数据库的表。
2.0 Mapping映射属性
Mapping是对索引库中文档的约束,常见的Mapping属性包括:
-
type:字段数据类型,常见的简单类型有:-
字符串:
text(可分词的文本)、keyword(精确值,例如:品牌、国家、ip地址) -
数值:
long、integer、short、byte、double、float、 -
布尔:
boolean -
日期:
date -
对象:
object
-
-
index:是否创建索引,默认为true -
analyzer:使用哪种分词器 -
properties:该字段的子字段
2.1 创建索引
DSL语法
PUT indexname
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name1":{
"type": "text"
},
"name2":{
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
参数说明:
settings:索引信息设置
number_of_shards:每个索引的主分片数,这个配置在索引创建后不能修改
number_of_replicas:每个主分片的副本数,这个配置可以随时修改。
mappings:索引映射定义
properties:字段定义 properties里是json配置,key为字段名称(自定义名称),value是个嵌套json,
type是指定字段的类型。
Java API
//从Spring容器获取client对象
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/createIndex")
public Boolean createIndex(String indexName) {
//创建索引请求类,构造函数参数为索引名称
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest(indexName);
//设置source映射字符串,直接把语句复制里面
request.source(
"{\n" +
" \"settings\": {\n" +
" \"number_of_shards\": 1,\n" +
" \"number_of_replicas\": 1\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"name1\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name2\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}",
XContentType.JSON);
try {
//调用创建索引语法
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
return true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
2.2 删除索引
DSL语法
DELETE indexname
Java API
//从Spring容器获取client对象
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/deleteIndex")
public Boolean deleteIndex(String indexName) {
//删除索引请求类,构造函数参数为索引名称
DeleteIndexRequest deleteIndexRequest = new DeleteIndexRequest(indexName);
try {
//调用删除索引语法
client.indices().delete(deleteIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
return true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
2.3 判断索引存在
DSL语法
HEAD indexname
如果索引存在,服务器将返回200状态码;如果索引不存在,服务器将返回404状态码。
200 - OK
Java API
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/existsIndex")
public Boolean existsIndex(String indexName) {
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest(indexName);
try {
return client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
2.4 开启/关闭索引
什么是 Elasticsearch 打开/关闭索引?
一旦索引被关闭,那么这个索引只能显示元数据信息,不能够进行读写操作。 再说说打开索引就好理解了。就是打开被关闭的索引,允许进行读写操作。
关闭索引
DSL语法
POST indexname/_close
调用执行,以下返回结果为成功
{ -
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"indices": { -
"indexname": { -
"closed": true
}
}
}
Java API
@RequestMapping("/closeIndex")
public Boolean closeIndex(String indexName) {
CloseIndexRequest closeIndexRequest = new CloseIndexRequest(indexName);
try {
client.indices().close(closeIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
开启索引
DSL语法
POST indexname/_open
调用执行,以下返回结果为成功
{ -
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true
}
Java API
@RequestMapping("/openIndex")
public Boolean openIndex(String indexName) {
OpenIndexRequest openIndexRequest = new OpenIndexRequest(indexName);
try {
client.indices().open(openIndexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
2.5 索引别名
索引别名概述:
给多个索引设置一个别名,可以使用这个别名同时查询多个索引的数据。
例如一个项目场景,每天要建立一个新的索引,程序要查询新的索引数据,程序必然要改变访问的索引名称,如果实现用户无感知切换,那么代码复杂度较高,很容易会对服务的使用者产生一定的影响,过程越复杂,BUG就越容易出现。
那么有了别名后,可以一开始就给索引加上这个别名,程序只关注访问这个别名,建立新索引后,把别名切换到新索引,程序不用变更,但是后续访问到了新的索引,并且无需停止应用的运行。当然这只是一个场景,在项目开发中,别名还有很多的用途,在后续项目讲解中我们会更多的介绍索引。
添加别名
创建索引别名,将别名
indexname_alias与索引indexname关联。
DSL语法
- 请求方式1
PUT indexname/_alias/indexname_alias
2.请求方式2
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "indexname",
"alias": "indexname_alias"
}
}
]
}
Java API
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/addAlias")
public Boolean addAlias(String indexName, String aliasName) {
IndicesAliasesRequest indicesAliasesRequest = new IndicesAliasesRequest();
IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions aliasActions = new IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions(IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions.Type.ADD);
aliasActions.index(indexName).alias(aliasName);
indicesAliasesRequest.addAliasAction(aliasActions);
try {
client.indices().updateAliases(indicesAliasesRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
删除别名
删除索引别名:解除别名
indexname_alias与索引indexname的关联。
DSL语法
- 请求方式1
DELETE indexname/_alias/indexname_alias
2.请求方式2
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"remove": {
"index": "indexname",
"alias": "indexname_alias"
}
}
]
}
Java API
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/removeAlias")
public Boolean removeAlias(String indexName, String aliasName) {
IndicesAliasesRequest indicesAliasesRequest = new IndicesAliasesRequest();
IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions aliasActions = new IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions(IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions.Type.REMOVE);
aliasActions.index(indexName).alias(aliasName);
indicesAliasesRequest.addAliasAction(aliasActions);
try {
client.indices().updateAliases(indicesAliasesRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
切换别名
切换一个别名是在同一个API中执行添加、删除操作。
DSL语法
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "indexname1",
"alias": "indexname_alias"
}
},
{
"remove": {
"index": "indexname2",
"alias": "indexname_alias"
}
}
]
}
Java API语法
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/changeAlias")
public Boolean changeAlias() {
String aliasName = "indexname_alias";
IndicesAliasesRequest indicesAliasesRequest = new IndicesAliasesRequest();
IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions addAliasActions = new IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions(IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions.Type.ADD);
addAliasActions.index("indexname1").alias(aliasName);
IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions removeAliasActions = new IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions(IndicesAliasesRequest.AliasActions.Type.REMOVE);
removeAliasActions.index("indexname2").alias(aliasName);
indicesAliasesRequest.addAliasAction(addAliasActions);
indicesAliasesRequest.addAliasAction(removeAliasActions);
try {
client.indices().updateAliases(indicesAliasesRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
查看别名
在 more 里选择 aliases 看所有索引的别名情况,这里也可以修改,功能非常的全面。
DSL语法
- 通过别名查询索引
GET _alias/indexname_alias
根据返回结果所示,indexname 索引下有这个别名
{ -
"indexname": { -
"aliases": { -
"indexname_alias": { -
}
}
}
}
2.通过索引查询别名
GET indexname/_alias
3.查看别名是否存在索引中
GET indexname/_alias/indexname_alias
Java API语法
1.通过别名查询索引
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/selectIndexByAlias")
public Map selectIndexByAlias(String aliasName) {
GetAliasesRequest getAliasesRequest = new GetAliasesRequest(aliasName);
try {
GetAliasesResponse response = client.indices().getAlias(getAliasesRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
Map<String, Set<AliasMetadata>> aliases;
aliases = response.getAliases();
return aliases;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
2.通过索引查询别名
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/selectAliasByIndex")
public Map selectAliasByIndex(String indexName) {
GetAliasesRequest getAliasesRequest = new GetAliasesRequest();
// 指定查看某一个索引的别名 不指定,则会搜索所有的别名
getAliasesRequest.indices(indexName);
try {
GetAliasesResponse response = client.indices().getAlias(getAliasesRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
Map<String, Set<AliasMetadata>> aliases;
aliases = response.getAliases();
return aliases;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
3.查看别名是否存在索引中
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/getAliasExist")
public Boolean getAliasExist(String indexName, String aliasName) {
GetAliasesRequest getAliasesRequest = new GetAliasesRequest(aliasName);
getAliasesRequest.indices(indexName);
try {
return client.indices().existsAlias(getAliasesRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
第三章 映射操作
映射信息会有索引的字段信息。
3.1 查看映射
新建索引后,后续开发中会需要看下有哪些字段,那么我们可以在客户端工具查看,也可以用命令查看。
1.在客户端中,选择 overview 找到要查看的索引,点击索引名,出现下拉框,选择 show mappings 就可以看到索引映射的字段信息了
DSL语法
GET indexname/_mapping
请求返回结果如下:
{ -
"indexname": { -
"mappings": { -
"properties": { -
"name1": { -
"type": "text"
},
"name2": { -
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
}
返回的信息和建立该索引时的信息是一致的。
Java API
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/getMapping")
public Map getMapping(String indexName) throws IOException {
GetMappingsRequest request = new GetMappingsRequest();
request.indices(indexName);
GetMappingsResponse mappingsResponse = client.indices().getMapping(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
Map<String, MappingMetadata> allMappings = mappingsResponse.mappings();
MappingMetadata indexMapping = allMappings.get(indexName);
Map<String, Object> mapping = indexMapping.sourceAsMap();
return mapping;
}
3.2 新增映射
映射一般情况下是创建索引的时候就已经指定好的,但是在实际开发情况下,我们需要新增字段,那么就需要新增一个字段映射,需要注意的是字段映射只能增加,不能更改删除。
DSL语法
POST indexname/_mapping
{
"properties":{
"name3":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
}
新增字段 name3 类型设置 keyword
返回以下结果说明成功:
{ -
"acknowledged": true
}
查询索引映射,返回结果如下:
{ -
"indexname": { -
"mappings": { -
"properties": { -
"name1": { -
"type": "text"
},
"name2": { -
"type": "integer"
},
"name3": { -
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
从返回结果可见,新字段映射已经添加成功。
Java API
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/addMapping")
public Boolean addMapping(String indexName) {
PutMappingRequest request = new PutMappingRequest(indexName);
request.source(
"{\n" +
" \"properties\":{\n" +
" \"name3\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"keyword\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}", XContentType.JSON);
try {
client.indices().putMapping(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
return true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return false;
}
第四章 文档数据操作(crud)
本章节我们讲对于ES数据的基本操作。
先创建一个索引,便于后续演示
PUT index_operation
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"age":{
"type": "integer"
},
"description":{
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
4.1 单条插入文档
指定ID插入数据时,ES会先拿着指定的id去对比一遍所有数据,如果没有新增,有则覆盖。
DSL语法
PUT index_operation/_doc/1
{
"name":"张三",
"age":18,
"description":"一个学习ES的学生"
}
添加一条指定ID为1的数据
ID可以手动指定,也可以自动生成
随机ID插入数据如下所示:
POST index_operation/_doc
{
"name":"李四",
"age":21,
"description":"一个学习Java的学生"
}
返回以下结果说明成功
{ -
"_index": "index_operation",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "TKc8a4sBNugPcqcoa9uX",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": { -
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1
}
我们发现ID变成了TKc8a4sBNugPcqcoa9uX,这是ES自动生产的ID
Java API
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/addDoc")
public Boolean addDoc() throws IOException {
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest().index("index_operation");
// 指定ID,也可以不指定随机生成
request.id("21");
// 这里用Map,也可以创建Java对象操作
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "张三");
map.put("age", 18);
map.put("description", "一个学习ES的学生");
// map转换json字符串
request.source(JSON.toJSONString(map), XContentType.JSON);
// 请求es
client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
return true;
}
4.2 批量插入文档
一般情况是用程序读取数据库执行插入,手动插入情况比较少见。
DSL语法
POST _bulk
{"create":{"_index":"index_operation","_id":4}}
{"name":"张三4","age":18,"description":"测试4"}
{"create":{"_index":"index_operation","_id":5}}
{"name":"张三5","age":18,"description":"测试5"}
Java API
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@RequestMapping("/addBatchDoc")
public Boolean addBatchDoc() throws IOException {
// 批量插入数据
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
// 生成10条数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 创建对象
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "张三");
map.put("age", 18 + i);
map.put("description", "一个学习ES的学生");
// 添加文档数据
IndexRequest source = new IndexRequest().index("index_operation");
source.source(JSON.toJSONString(map), XContentType.JSON);
request.add(source);
}
// 请求es
client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
return true;
}
4.3 通过ID查询文档
4.4 条件查询文档
4.5 单条更新文档
4.6 批量更新文档
4.7 条件更新文档
4.8 单条删除文档
4.9 条件删除文档
第五章 字段类型介绍
5.1 索引方式
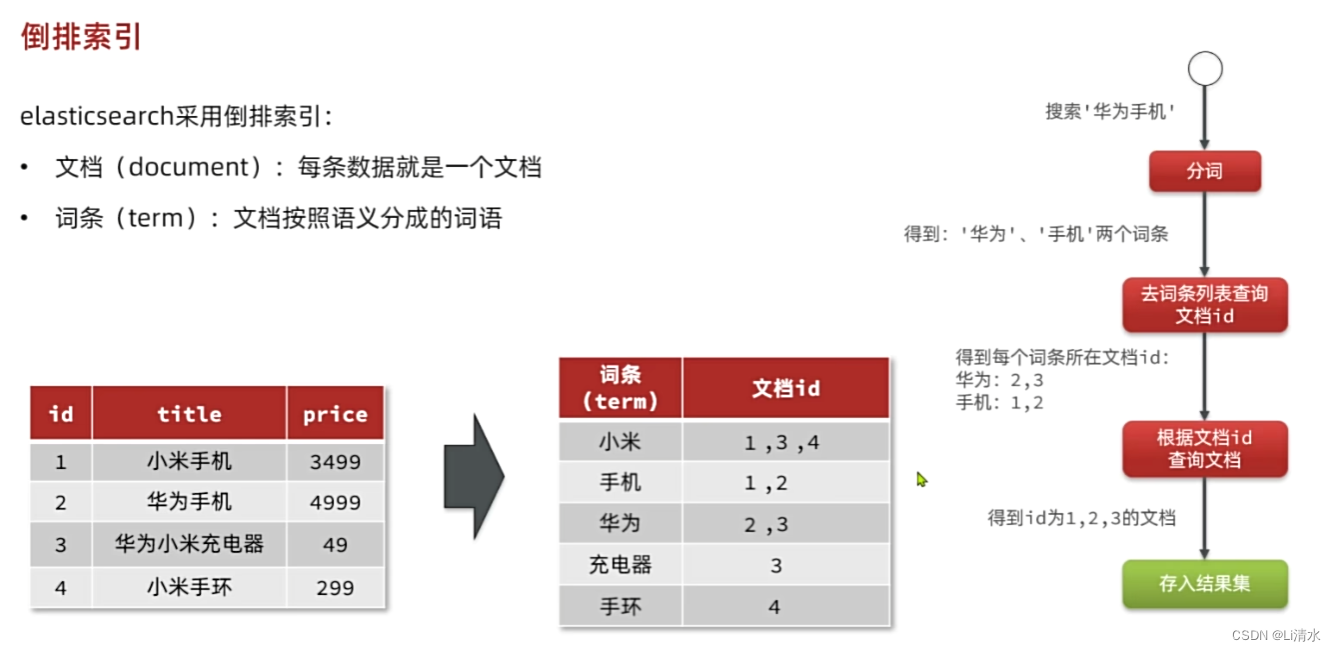
正向索引
正排索引是以文档的ID作为关键字,并且记录文档中每个字段的值信息,通过查询id来把整条文档拿出来。
但是在查询某一个keyword存在于哪些文档的时候, 需要对所有文档进行扫描匹配。这样检索效率比较低下。
倒排索引
 第六章 分词操作
第六章 分词操作
6.1 IK分词器
IK分词器包含两种模式:
-
ik_smart:智能语义切分 -
ik_max_word:最细粒度切分
我们在Kibana的DevTools上来测试分词器,首先测试Elasticsearch官方提供的标准分词器:
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "黑马程序员学习java太棒了"
}结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "黑",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "马",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "程",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "序",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "员",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "学",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "习",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "java",
"start_offset" : 7,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "太",
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "棒",
"start_offset" : 12,
"end_offset" : 13,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 9
},
{
"token" : "了",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 14,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 10
}
]
}
可以看到,标准分词器智能1字1词条,无法正确对中文做分词。
我们再测试IK分词器:
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"text": "黑马程序员学习java太棒了"
}执行结果如下:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "黑马",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "程序员",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "学习",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "java",
"start_offset" : 7,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "ENGLISH",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "太棒了",
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 14,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
6.2 拓展词典
随着互联网的发展,“造词运动”也越发的频繁。出现了很多新的词语,在原有的词汇列表中并不存在。比如:“泰裤辣”,“传智播客” 等。
IK分词器无法对这些词汇分词,测试一下:
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "传智播客开设大学,真的泰裤辣!"
}结果:
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "传",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "智",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "播",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "客",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "开设",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "大学",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 8,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "真的",
"start_offset" : 9,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "CN_WORD",
"position" : 6
},
{
"token" : "泰",
"start_offset" : 11,
"end_offset" : 12,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 7
},
{
"token" : "裤",
"start_offset" : 12,
"end_offset" : 13,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 8
},
{
"token" : "辣",
"start_offset" : 13,
"end_offset" : 14,
"type" : "CN_CHAR",
"position" : 9
}
]
}
可以看到,传智播客和泰裤辣都无法正确分词。
所以要想正确分词,IK分词器的词库也需要不断的更新,IK分词器提供了扩展词汇的功能。
1)打开IK分词器config目录:
2)在IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml配置文件内容添加:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd">
<properties>
<comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 *** 添加扩展词典-->
<entry key="ext_dict">ext.dic</entry>
</properties> 3)在IK分词器的config目录新建一个 ext.dic,可以参考config目录下复制一个配置文件进行修改
传智播客
泰裤辣4)重启elasticsearch
docker restart es
# 查看 日志
docker logs -f elasticsearch
本站资源均来自互联网,仅供研究学习,禁止违法使用和商用,产生法律纠纷本站概不负责!如果侵犯了您的权益请与我们联系!
转载请注明出处: 免费源码网-免费的源码资源网站 » Elasticsearch搜索引擎(初级篇)

发表评论 取消回复