目录
1、 2.两数相加
1.1 算法原理
解题的核心就是, 记录两节点数值之和, 并保留进位信息:
- tmp // 记录两节点相加之和 => tmp += cur1.val + cur2.val;
- tmp % 10 // 表示该位应得值(新节点的值) => tail.next = new ListNode(tmp % 10);
- tmp /= 10 // 表示下一位的进位
1.2 算法代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = newHead;
int tmp = 0;
ListNode cur1 = l1;
ListNode cur2 = l2;
while(cur1 != null || cur2 != null || tmp != 0) {
if(cur1 != null) {
tmp += cur1.val;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
if(cur2 != null) {
tmp += cur2.val;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
tail.next = new ListNode(tmp % 10);
tail = tail.next;
tmp /= 10;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}2、24.两两交换链表中的节点
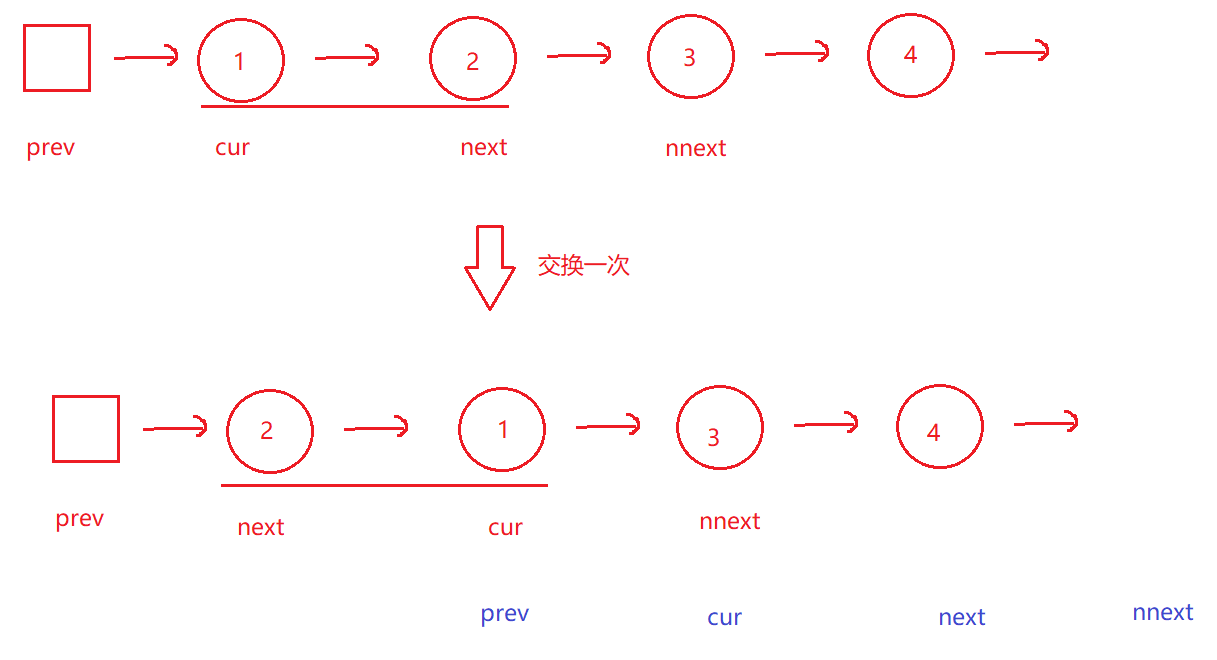
2.1 算法原理
每翻转两个节点, 需要修改四个引用的指向, 定义4个变量:
- 当 cur 为 null, 或者 next 为 null 时, 说明链表已全部翻转完成.
- 其中 next 以及 nnext 的更新, 涉及空指针异常, 需要额外判断
 2.2 算法代码
2.2 算法代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution1 {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0, head);
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode prev = newHead, cur = head, next = cur.next, nnext = next.next;
while(cur != null && next != null) {
// 两两交换
prev.next = next;
next.next = cur;
cur.next = nnext;
// 后续
prev = cur;
cur = nnext;
if(cur != null) next = cur.next;
if(next != null) nnext = next.next;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}3、143. 重排链表
3.1 算法原理
核心思想:
- 找链表的中间节点, 根据中间节点分割链表(快慢双指针).
- 将第二个链表逆序(头插法)
- 依次合并两个链表
 3.2 算法代码
3.2 算法代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode flg = slow;
ListNode head2 = new ListNode();
while(slow != null) {
ListNode next = slow.next;
slow.next = head2.next;
head2.next = slow;
slow = next;
}
ListNode cur1 = head, cur2 = head2.next;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = newHead;
// slow 是要逆序的链表(第二个链表)中的, 第二个链表更长
while(cur2 != null) {
// 第一个链表的结尾指向不为 null
if(cur1 != flg ) {
tail.next = cur1;
tail = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
tail.next = cur2;
tail = cur2;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
}
}4、合并 K 个升序链表
4.1 算法原理 --- 解法一
暴力的思想, 一个一个的进行合并, 时间复杂度直逼 O(n^3) => 不推荐
4.2 算法原理 --- 解法二
借助优先级队列(小堆), 将每个链表中最小的元素入堆, 选出值最小的那个节点, 进行出堆操作(接着将下一个节点入堆), 并将这个最小的节点拼接到新链表中.
- 由于 k 个链表一共有 k*n 个元素, 且使用队列选出最小元素后, 队列会进行O(logK)级别的调整, 最终, 可将时间复杂度优化为 O(N*K*logK)
4.2.1 算法代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists.length == 0) return null;
// 建小堆
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((v1, v2) -> v1.val - v2.val);
// 将每个链表中最小的节点放到堆中
for (ListNode node : lists) {
// 节点可能为空
if(node != null)
queue.offer(node);
}
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = newHead;
// 堆为空时, 说明合并完成
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
ListNode node = queue.poll();
tail.next = new ListNode(node.val);
tail = tail.next;
if(node.next != null) {
queue.offer(node.next);
}
}
return newHead.next;
}
}4.3 算法原理 --- 解法三
以递归方式, 采用 归并排序的思想, 进行合并.
时间复杂度同样可优化为: N*K*O(logK)
- K 条链表, 递归 logK 层, 每层需要合并 K 次, 每次合并有 N 个节点. => N*K*O(logK)
4.3.1 算法代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if(lists.length == 0) return null;
return mergeSort(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
public ListNode mergeSort(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {
if(left >= right) return lists[right];
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
ListNode cur1 = mergeSort(lists, left, mid);
ListNode cur2 = mergeSort(lists, mid + 1, right);
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
ListNode tail = newHead;
while(cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {
if(cur1.val <= cur2.val) {
tail.next = cur1;
tail = tail.next;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}else {
tail.next = cur2;
tail = tail.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
}
if(cur1 != null) {
tail.next = cur1;
}
if(cur2 != null) {
tail.next = cur2;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}5、K 个一组翻转链表
5.1 算法原理
- K 个节点为一组, 进行翻转操作: 节点总个数 n / K => 得到一共要翻转的组数
- 每一组通过头插法进行翻转操作
- 细节点: 需要记录每组链表的头结点, 将翻转后相邻两组的链表进行连接
5.2 算法代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
int n = 0;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
n++;
cur = cur.next;
}
// 翻转多少组
n /= k;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
// 每组链表的头结点
ListNode prev = newHead;
ListNode now = head;
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 记录头结点
ListNode tmp = now;
while(count != k) {
ListNode next = now.next;
now.next = prev.next;
prev.next = now;
now = next;
count++;
}
prev = tmp;
count = 0;
}
// 连接后续不需要翻转的节点
prev.next = now;
return newHead.next;
}
}END
本站资源均来自互联网,仅供研究学习,禁止违法使用和商用,产生法律纠纷本站概不负责!如果侵犯了您的权益请与我们联系!
转载请注明出处: 免费源码网-免费的源码资源网站 » 算法专题:链表

发表评论 取消回复